17 SEO Myths That You Should Never Follow
How did I increase my search traffic by 13.15% in just 30 days?
I followed a proven plan, tapped into a hungry market, created in-depth content that’s backed up by stats and data, solved a definite problem and promoted the blog posts. This strategy seems so basic, but that’s how to win at SEO.
The reality is that search traffic converts 9% better than social media traffic. But, in order to get it, you have to stop believing in some myths.
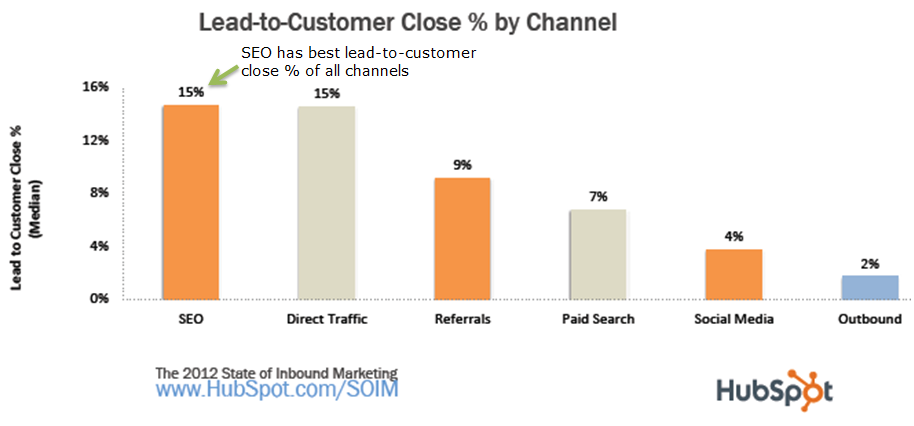
These SEO myths tend to keep hardworking content marketers and bloggers from improving their search traffic and rankings.
Some SEOs claim they’re affiliated with Google. That’s a big myth, because Google doesn’t disclose who their SEO partners and affiliates are. So, if an SEO consultant or agency promises you top rankings for the “low” price of $499 per month, that’s a SCAM. No one can guarantee top Google rankings.
Without further ado, here are the 17 SEO myths that you should ignore. I’ve also provided tips on what advice you should follow.
Download this printable checklist to stay away from these SEO myths.
In no particular order, the myths are:
1. Keyword targeting became irrelevant after Google Hummingbird
Hummingbird changed the future of search. It prompted content producers to adopt a new mindset that will benefit the end-user. If keywords are still showing on Google’s first page, it’s an indication that they still matter.
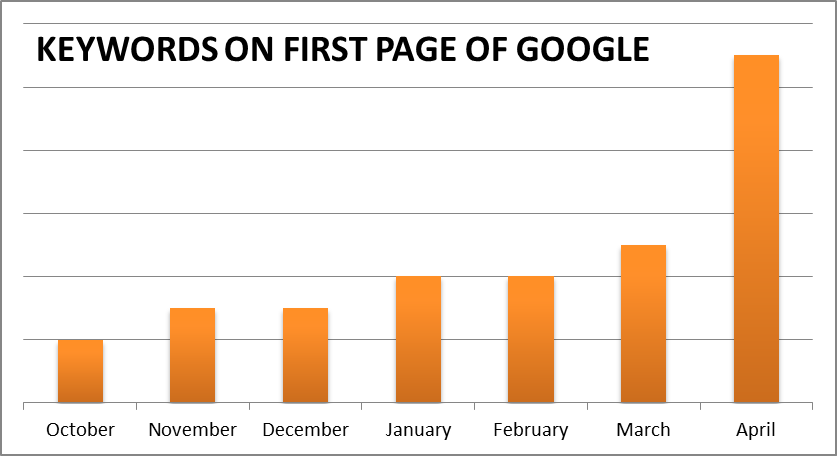
According to Matt Cutts, Head of the WebSpam Team at Google, 90% of searches were predicted to be impacted by Hummingbird, which wasn’t an update like Panda and Penguin, but rather a total revamp of the search algorithm.

Rand Fishkin, founder of Moz, said that less than 15% of the ranking equation is wrapped up in keyword targeting. Instead, he suggested focusing on offering unique value, rather than unique content, which is what SEOs tried to achieve before.
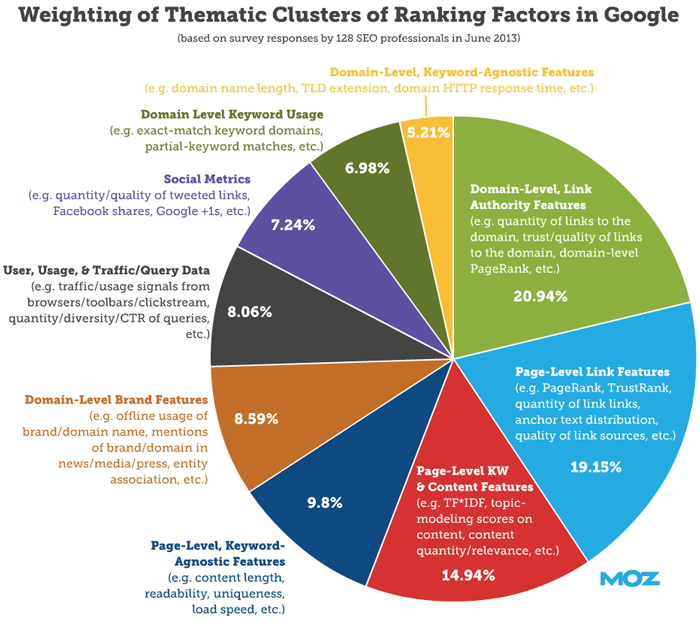
However, it would be wrong to say that targeting relevant keywords in your content is no longer useful at all.
Keyword research and targeting have actually become easier, because with Hummingbird. You don’t have to worry about obeying a certain keyword ratio. Instead, focus on searcher intent.
For example, why would someone search for “small business CRM tool”?
- Does the person want to buy a CRM tool?
- Is the person looking to read some honest reviews?
- Is the searcher a beginner who doesn’t even know what CRM stands for?
What the Hummingbird algorithm change really did was stress to us the importance of knowing the reason behind a particular keyword and creating content to meet that need.
This means that keywords are still important, because without them, you can’t know the searcher’s intent.
Several authority platforms, such as Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, Pinterest and others, rely on keyword targeting to meet users’ needs.
It’s almost impossible to find exactly what you’re looking for, except by using keywords to search. According to Brian Dean, “Keywords are like a compass for your SEO campaigns; they tell you where to go and whether or not you’re making progress.”
2. Having an XML sitemap will boost your search rankings
Have you installed the Google XML Sitemaps generator on your WordPress site? Can a sitemap boost your search rankings? In the ranking factors below, you won’t find XML sitemaps anywhere sony bravia spotify herunterladen.

But, a XML sitemap is necessary, if you want to build a crawlable site. Each time you create a new post or edit an existing post, the Google XML sitemaps generator will create an updated sitemap with your new pages and submit it to Google and other search engines.
Casey Henry experimented with sitemaps to find out whether they can boost search rankings. What he found surprised him.
When he installed the Google XML sitemaps generator on a client’s website, it took an average of 14 minutes for Google to index new pages.
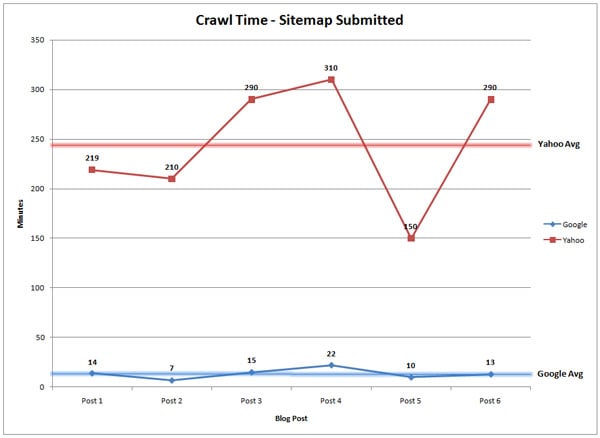
Before he installed the sitemaps generator, it took 1,375 minutes.
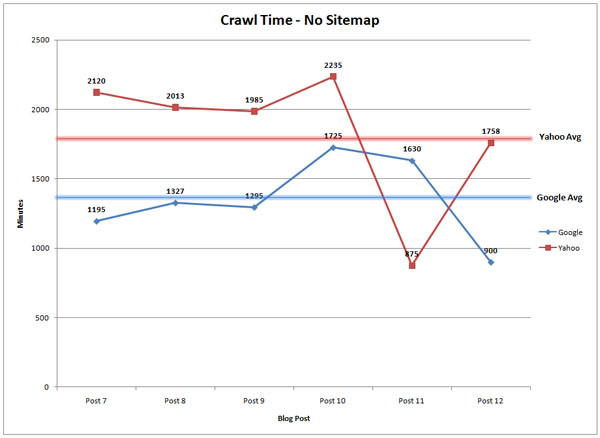
So, we know that an XML Sitemap helps search engines to crawl and index fresh pages faster. But, does it improve search rankings?
Well, way back in 2008, Trevor Foucher and Susan Moskwa of the Webmaster Tools Team spoke as part of the Sitemaps Panel at Search Engine Strategies in Chicago. One of the many questions they were asked was, “Will a sitemap help me rank better?”
Here’s Trevor’s answer: A sitemap truly doesn’t affect the actual rankings of your web pages. Sitemaps are like an aid – a guide that gives more information about your site to Google, such as making sure that all of your URLs are indexed for easy crawling.
Of course, it can lead to more visibility for your site eventually, when the URLs are prioritized. But, that is not a guarantee.
A quick tip: If you’re not already using the Google XML Sitemaps generator on your WordPress site, you should install it now. There’s no guarantee that your rankings will improve. But, it will help Google discover your fresh content faster.
3. Meta tags don’t matter
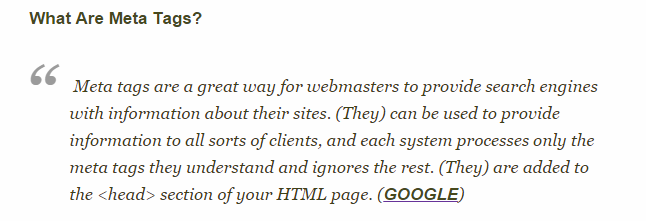
Meta tags are HTML tags that appear in between the opening and closing <head> tags. They’re used to show preview snippets for a specific webpage in the search results.

There has been a lot of debate in the SEO world about the impact of meta tags, especially post-Hummingbird.
Interestingly, Danny Sullivan wrote an in-depth article on the “death of meta tags,” in order to further discuss the state of meta tags and why they may not be that useful in today’s SEO.
The 3 elements of a meta tag are:
- The title tag
- The meta description
- Keywords
Note: The title tag appears in the <head> section of a web page, but it’s a necessary page element. The meta description and keywords, on the other hand, are optional page elements. Without the meta description, though, Google may pull text from the page body as a preview snippet.
Matt Cutts has said that Google doesn’t use the keywords meta tag in page rankings. Nevertheless, meta tags are still relevant and it makes sense to spend time on them.
Adding meta tags may not boost your search rankings, but meta tags help to tell users and search engines what your site is about, says Kristine Schachinger.
Meta tags will also make your search results attractive, which can attract more clicks from search users.
You can take care of keywords, title tags and descriptions with the All In One SEO WordPress plugin.
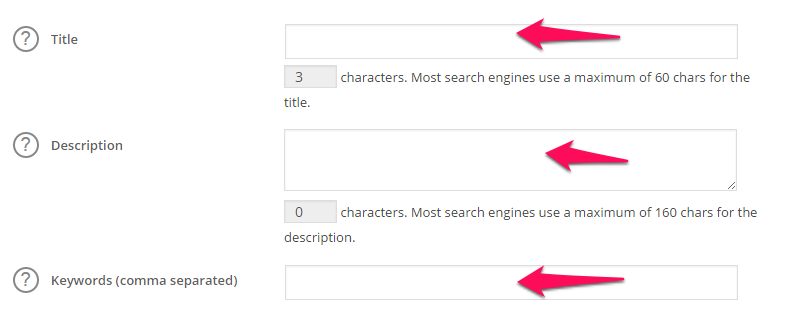
To create rich meta descriptions, use these tips:

4. Use meta robots tag to specify indexable pages
The Robots.txt file tells search engine bots which sections (pages, links, etc.) of your site to crawl and index and which to ignore herunterladen.
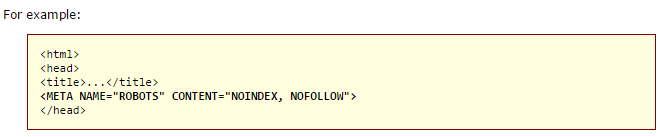
The source code looks like this, in your HTML file:
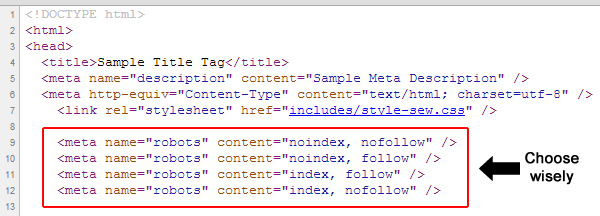
However, you can easily set noindex and nofollow tags, using the Yoast or All in One SEO WordPress plugins.

Note: You should only check the NOINDEX button if you’re certain that you want the page to be private and not viewable for the public.
So, does this mean that without specifying the meta robots tag, Google will not find your fresh pages?
I don’t think so. I can’t remember the last time that I specified which pages Google should index. Unless you want to make specific pages private, there is really no need to go through the hassle.
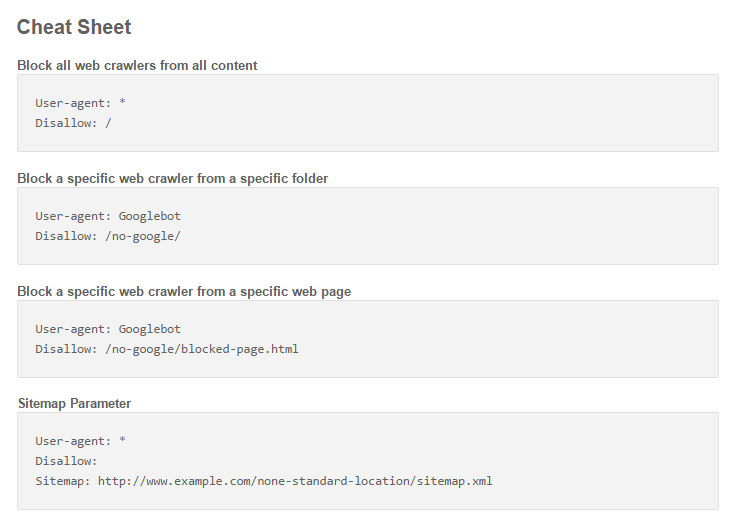
You can use the Robot.txt file to block all web crawlers from all of your content, a specific folder or a specific webpage.
But, if you don’t need to block web crawlers, then don’t bother. Save your time and channel it towards something more important.
5. Top-level domains improve rankings
A top-level domain occupies the highest position in the hierarchical domain name system. Most search users will recognize .com as a website extension, but may be confused when they find .biz or .guru.
This is partly because when you type any keyword phrase into Google search, 98% of the search results are .com domain names. Let’s see:
The only exception that I know of is geo-targetable country domains. If I live in Canada, but have a .com domain name, Google will assume that my audience is global and show my web pages in their search results to the global audience.
On the other hand, a Canadian site in the same industry with a .ca extension will show up primarily for search users from that country.
In terms of conversions, .com domains have achieved tremendous results for many people.
In 2007, prior to Google algorithm updates, ICANN introduced new generic top-level domain names – for example, .guru, .club, .company and.email.

But, .com still trumps all of them, in terms of global usage.
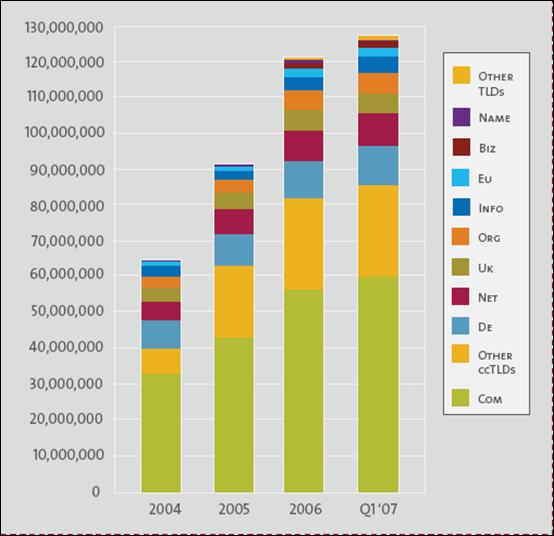
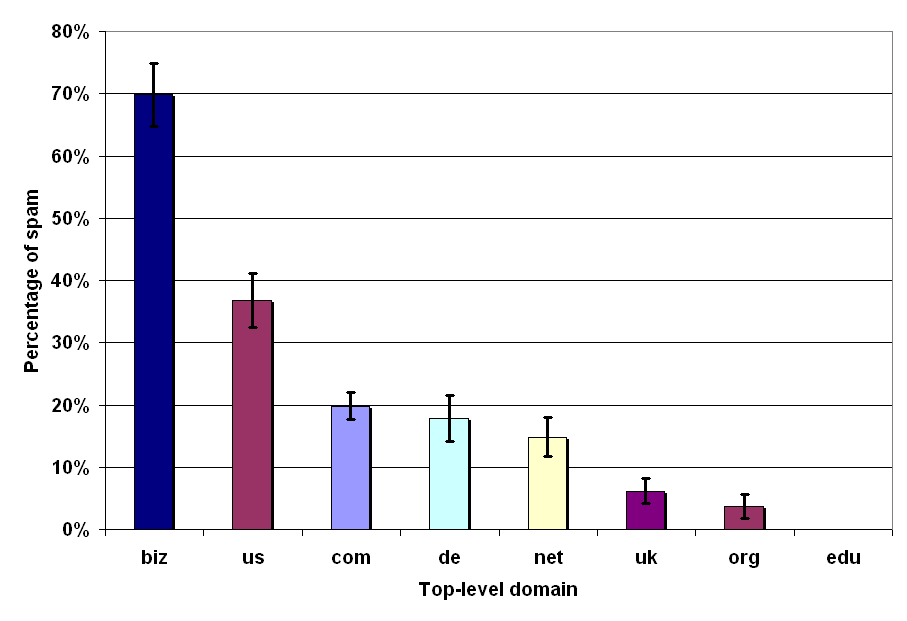
Alexandros Ntoulas and his team found that top-level domains are the major culprits of web spam.
Their research showed that .biz, .us and .com domains are the three biggest propagators of web spam. And, this includes links that Google uses to rank web pages in their search engine.
Will the new TLDs affect SEO? Well, it’s too early to know, but here’s what Matt Cutts and Dr. Pete Meyers had to say:
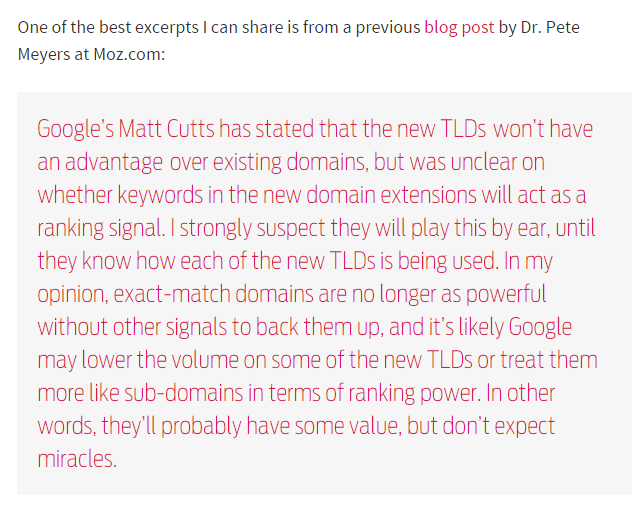
The major factor in whether TLDs have an effect on SEO is whether or not the domain contains keywords. Of course, you and I know that Exact Match Domain names risk getting penalized.
Everything still boils down to the value that you offer with your domain name. During the days of frequent updates, an average EMD ranking dropped from 13.4% to 26.6%.
This data shouldn’t scare you, but rather it should guide you. Now you know that when choosing top-level domains, what matters is the long-term brand and benefit when you register a memorable and professional domain name herunterladen.
The caveat: If you haven’t registered any domain name yet, I’d advise you to choose top-level domain names (.com and .net).
However, if you’re already a site owner, just decide to focus on offering immense value, creating high-quality content and using social media to connect influencers who will help promote your content. I’ve even seen domain names with weird extensions do well in search, such as Paper.li.
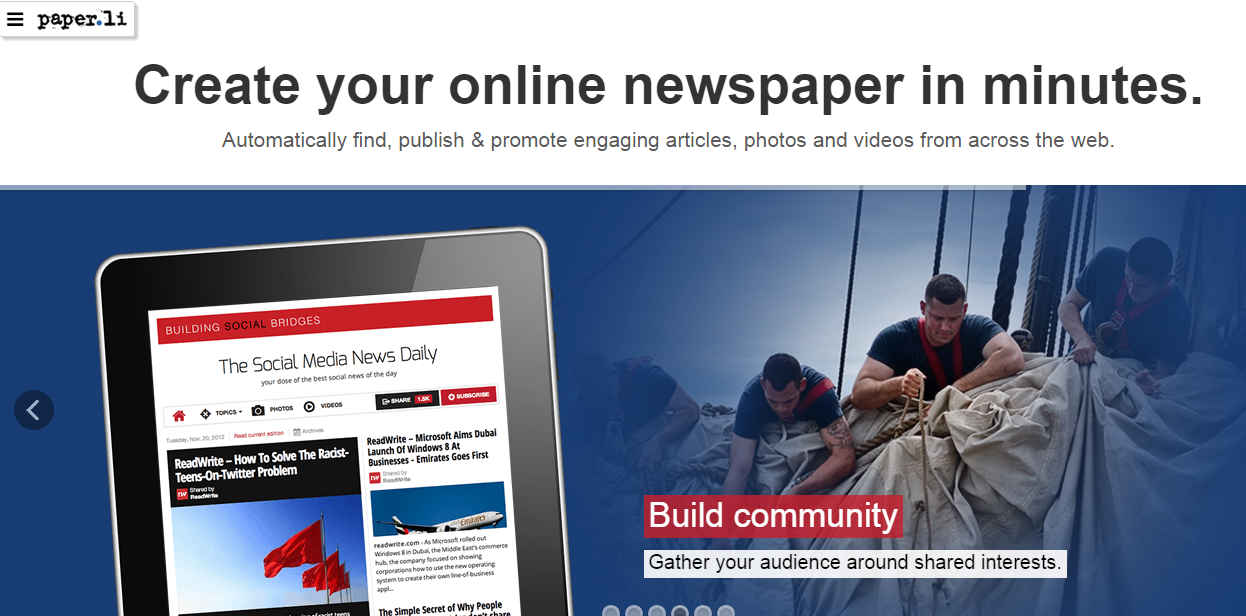
In fact, this site currently ranks #4 for a high-volume keyword (create a newspaper online) with lots of competition.
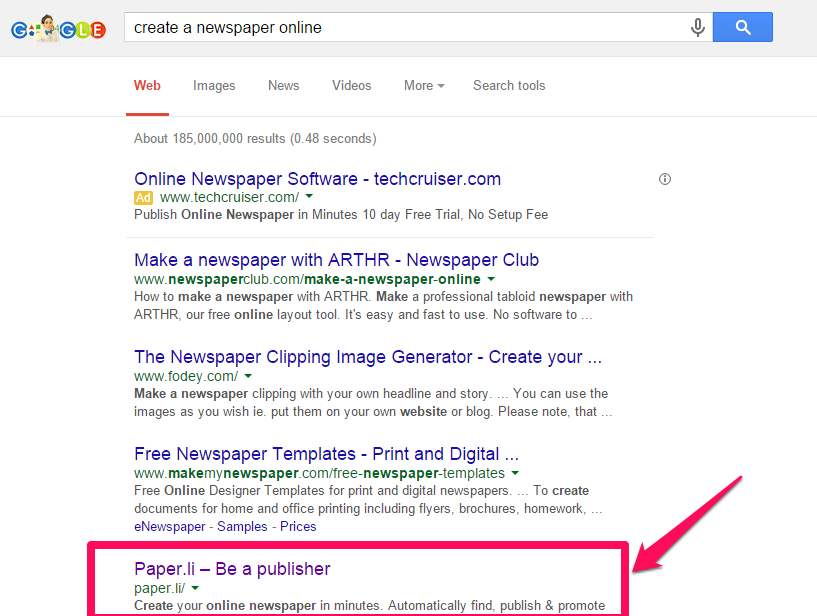
This clearly shows that it’s no longer about the top-level domain extensions, but the value your site offers.
6. Including a target keyword in anchor text no longer matters in SEO
When building links, should you use keywords in your anchor text?
Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink (e.g. Neil Patel). The anchor text enclosed in the bracket is “Neil Patel.” When clicked, that phrase takes the user to the blog.
Many industry experts believe that anchor text will remain a ranking factor forever, no matter what changes come with the next Google update.
So, is keyword-rich anchor text still helpful in boosting your rankings?
The goal of every algorithm update or change is to help searchers find the right sites that contain the information they need, in a user-friendly manner.
Over-optimization can get you penalized by Google. Before Google Penguin, you could use keyword-rich anchor text on your blog posts, both for internal linking and external linking (i.e., linking to other sites).
However, there is a slight change now. Of course, contextual links have 5-10x more ranking power than your usual author profile link that appears in your guest posts, for example.
But, excessive use of keyword-rich anchor text will negatively affect your site rankings. Cross-linking with rich anchor text is equally risky, so avoid it.
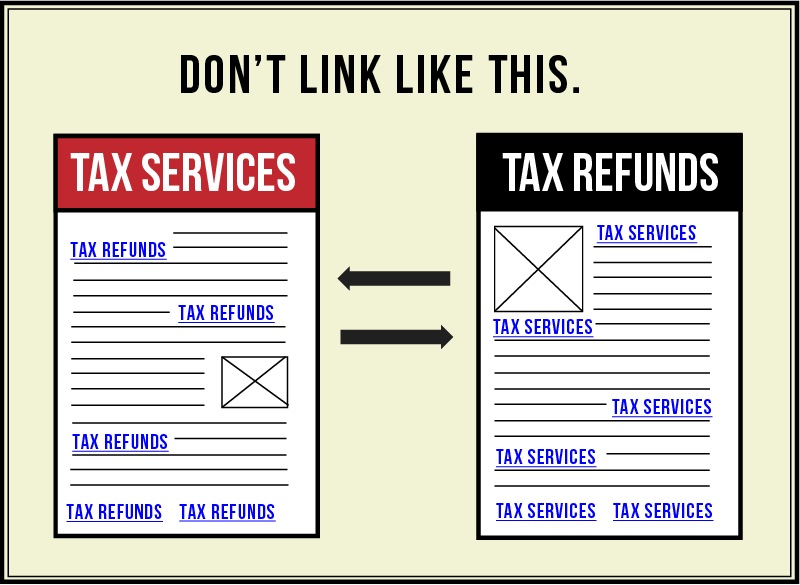
But, to say that keyword-rich anchor text will no longer be relevant in search rankings isn’t accurate. In other words, it’s a myth.
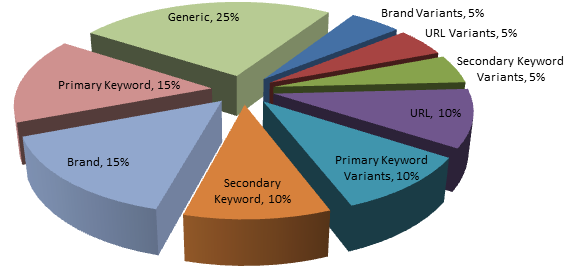
Change your approach. Diversify anchor text and make sure that your primary and secondary keywords, as well as your brand, URL and generic keywords are used as anchor texts.
Personally, I like building natural links, because that’s what Google wants. You can’t be smarter than the engineers who spend their workdays making the algorithm work smarter. So, stay off Google’s radar and avoid a penalty.
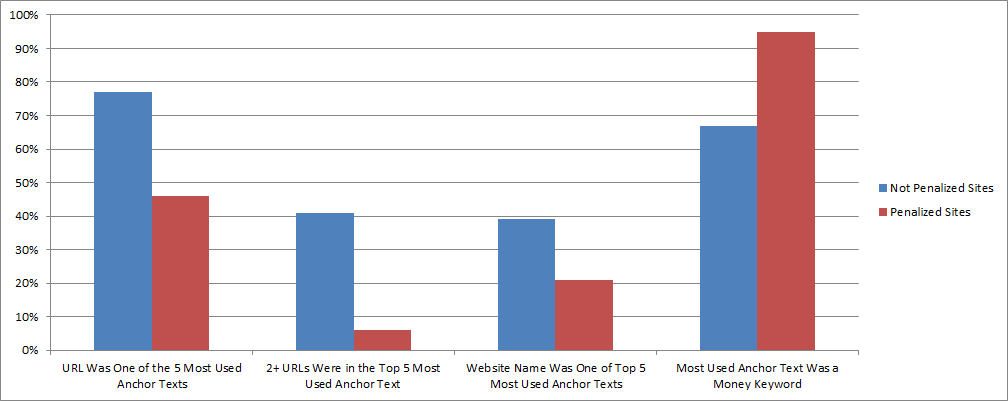
After the Penguin update, most sites with optimized anchor text got penalized. On the other hand, those sites with diversified anchor text experienced a boost and only a few of them were negatively affected.
There are several types of anchor text that you can use, but let’s drill down and determine what works best.
First, recognize that brand building is the easiest way to stand out positively in Google’s eyes. So, you can follow this anchor text strategy:

In summary, the three types of anchor texts that you should focus on are:
i). Natural anchor text: It could be keyword-rich, brand or URL anchor text, but it should flow naturally with the rest of the content. These are mostly editorial links and will definitely impact your rankings. For example:

Matt Cutts has been advocating natural anchor text for a long time youtube für pc downloaden. It works, because Google’s primary objective is creating the best search experience for its users.

ii). Brand name or brand URL anchor text: If you can build more brand or URL anchor text, you should be fine. Aim for branded anchor text in roughly 90% of your links.
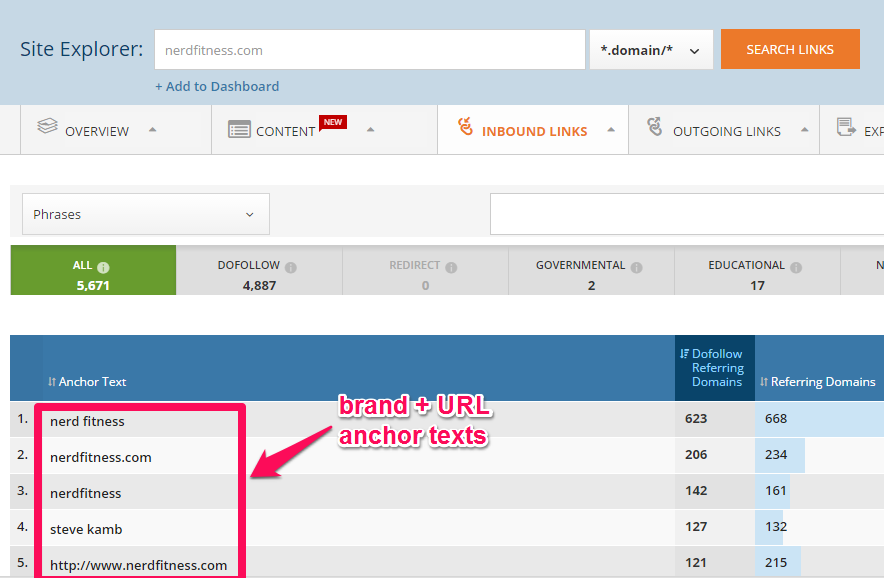
For example, NerdFitness is an authority site for fitness enthusiasts. There are thousands of keywords that the author could use to build links, but he doesn’t.

Instead, most of the anchor text pointing to his pages is either brand name, brand URLs or naked URLs (for example, nerdfitness.com).
SmartPassiveIncome also has more branded and URL anchor text.
Of course, you can’t possibly control what anchor text another person uses to link to your web page. But, if you have the opportunity, either through guest blogging or interviews, steer clear of keyword-rich anchor text.
Or, better yet, use your brand name + keyword (e.g., Brian Dean’s Link Building).
You can also use branded URLs as your anchor text (e.g., “To learn more about growth hacking, visit: http://neilpatel.com.”)
iii). Generic anchor text: This is often referred to as a “noise anchor.” Don’t use it excessively, because it could turn out to be over-optimized.
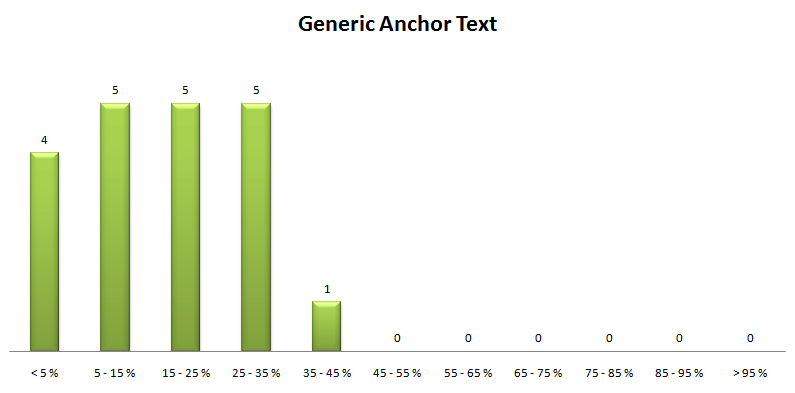
According to Search Engine Watch, over half of all anchor text has one to three words in it. This means that when using generic keywords, you should move from one word to three or more (e.g., learn more here, visit the site, see the homepage, check it out, get started today).
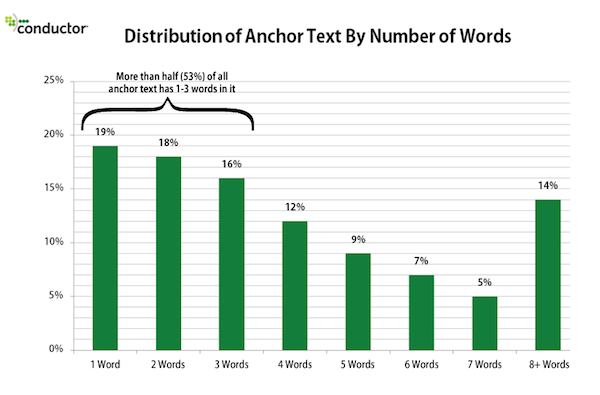
At least 5% of your anchors should be generic, especially when you’re linking out or from an irrelevant page.
For example, if I want to make a reference to a sports website from my internet marketing blog, I would use generic keywords.
See how that might look in the paragraph below:
When I started blogging, I was getting it all wrong, until a friend of mine from Canada, who runs a sports website advised me to narrow my niche and focus on a small group that has potential. Do you want to give him a shout out? Click here.
Bottom line: Keyword-rich anchor text is still important, but use this approach wisely and diversify where you can.
7. Google will find your fresh content and index it
Crawl optimization is an important topic that I’ll expand on in a future article. For now, let’s say that it refers to the things that you can do to help Google discover, crawl and index your fresh content easily.
Search engine bots feed on fresh content. When your new article is live, it means that you’ve prepared a meal for them. But, does that mean that your fresh content will be crawled and indexed without your input?
Sure, it can happen – but it may take up to two days, especially if your blog is fairly new. To get the ball rolling, you should help the search spiders discover your fresh content.
That’s one of the benefits of installing a Google XML sitemap generator plugin for WordPress. You don’t have to do anything, once you set up the plugin.
The moment you press the “publish” button, a new XML sitemap is generated and sent to the major search engines and directories. This is not manipulative at all and it helps Google index your new content as quickly as possible.
Updating your social profiles will get your fresh content indexed faster. It’s very simple, just share your link on your Facebook page or tweet it.
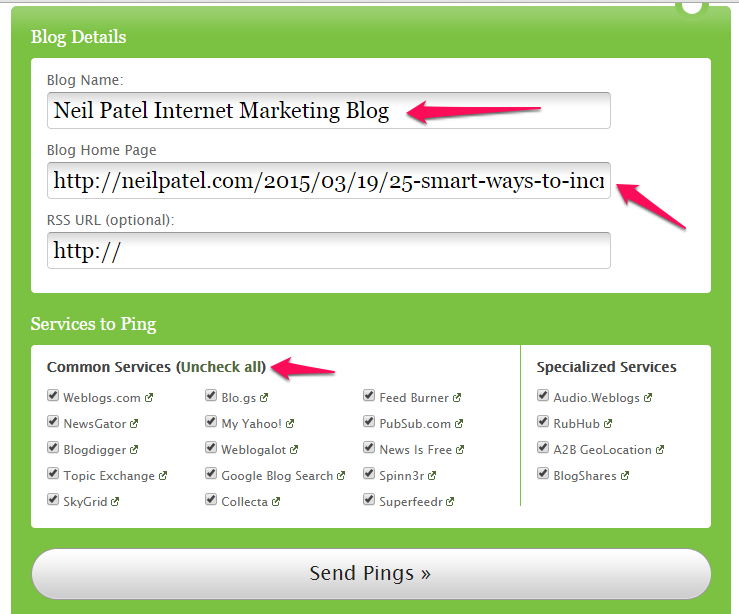
Another simple tool that works for me is Pingomatic adobe flashplayer herunterladen. It let’s you quickly ping a bunch of web services to notify them of your new content. Using this free service gets my fresh content indexed within six hours.
8. Hire an SEO agency to get top rankings fast
This is the most interesting myth of all. How could any SEO agency or expert guarantee top Google rankings in this age?
Sure, there are various reasons why you might need an SEO agency, especially for keyword analysis and competitive auditing. “Quick rankings” is not one of those reasons.

The truth of the matter is that Google handles over 100 billion searches per month. Since no SEO can predict tomorrow’s keywords, it’s almost impossible for anyone to guarantee fast search rankings.
Nearly eight years after I wrote my very first blog post, my blog gets over 700,000 visitors a month. I’ve published 614 blog posts in that time.
I know there are several blogs out there with a fraction of the content that I’ve published, which nevertheless generate more traffic each month. This tells you that several factors impact your Google rankings, including timing.
I never promise clients that I have a magic bullet, when it comes to SEO and ranking. Sure, I know the best approach to take, if I want to improve my clients’ rankings, especially through long-tail keywords. But, I can’t guarantee top rankings.
Listen up: SEO is a long-term practice. If you’re desperate to rank in Google’s top 10 overnight or a few months after starting your blog, you’re making a very big mistake.
Aged domain names, authority links and in-depth content can all help boost rankings, but they’re not guarantees, either. There are so many sites out there that have fulfilled these requirements, but still struggle to rank well in Google results.
If you’ve got funds in your marketing budget, there are some good reasons to hire an SEO agency:
- You don’t have the time to run your site.
- You’re looking to improve your search traffic.
- You want help with long-tail keywords research.
- You want to stay up to date in the SEO industry.
- You want to be trained by an agency.
But, you should not hire an SEO agency that promises to give you top rankings fast. Even if they somehow succeed at pushing your site to the #1 position, without a strong foundation your rankings will slide and you’ll lose more than you gained.
SEO is for long-term-oriented digital entrepreneurs who have made up their minds to help users find the answers they need.
9. Guest blogging is dead
There was an uproar, in 2014, when Matt Cutts said that “if you’re using guest blogging as a way to get links … stop.” A lot of SEOs who didn’t understand exactly what that statement meant immediately started preaching against guest blogging.

There is no technical difference between guest-blogging content and any other type of content. Guest blogging simply means that a guest contributed a piece of content to your blog.
What Matt Cutts is talking about is crappy content on blogs from an outside author. But, even where the author was the site owner, Google’s Panda update had already begun punishing low-quality content.
Search engines index billions of web pages, from different domain names, IP addresses, locations and so on. And, these web pages are owned by different people. That’s interconnectivity at work.
Think about it: the content on high authority sites is regularly contributed by freelancers and outside authors! Sites like the New York Times, eHow, BusinessWeek, Inc., CNN and Mashable all rely on content written not by the “site owner” alone, but by hundreds of other people herunterladen.
When it comes to guest blogging, it’s neither the guest nor even the content that’s the problem, but the context: the type of article, its uniqueness, the anchor texts and the links pointing to and from the site.
Personally, I believe that guest blogging is not dead. And, it’s never going to die, because Google can’t accurately decipher what a “guest post” is, especially when the author’s link is right inside the body and not on the author profile.
One of the ways I grew my blog traffic by 206% was through guest blogging. It also helped Louis Gudema with SEO.
Even Matt Cutts himself later endorsed guest blogging:
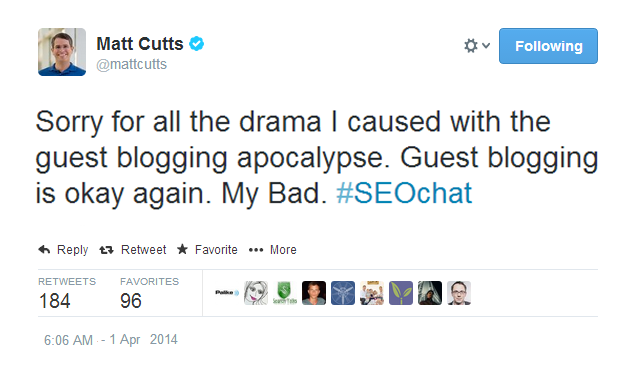
On that note, I still recommend guest blogging, as long as you follow these simple tips:
- Avoid spammy blogs: If the blog doesn’t have unique content, avoid it.
- Don’t call them “guest posts”: This is important. Google can find the text “this is a guest post.” Instead, write as though you’re an in-house contributor. It doesn’t matter where the guest comes from, as long as the post is useful.
- Build relationships, not links: Don’t try to get your guest post published on a trusted blog, just because of the link. If that’s your mindset, you’ll miss out on the relationship.
- Build your brand: Use your brand name or URL as anchor text for natural link building.
- Contextual links: As much as possible, try to keep your links within the content, not in the author profile where it doesn’t carry as much weight.
- Use guest blogging carefully: Focus on the end users. Create content that makes them think – that resonates with them and solves their problem. Engage them, reply to comments and build your email list.
10. Keyword research is not necessary
This myth is just as dangerous as the first. As a content marketer and blogger, you can’t afford to ignore keyword research.
No Google update eliminated the importance of keywords. Obviously, if every other factor is present, you’ll likely get more clicks, when your web page shows at the top.
What you should avoid is over-optimization, excessive use of keyword-rich anchor texts and Exact Match Domain updates. Focus on ROI, instead of the top rankings for that keyword. After all, whether you rank #1 or #5, what matters is what you get back.
Google’s Keyword Planner is still the most accurate keyword research tool out there. Most other tools rely on Google. Those other tools are still helpful, though.
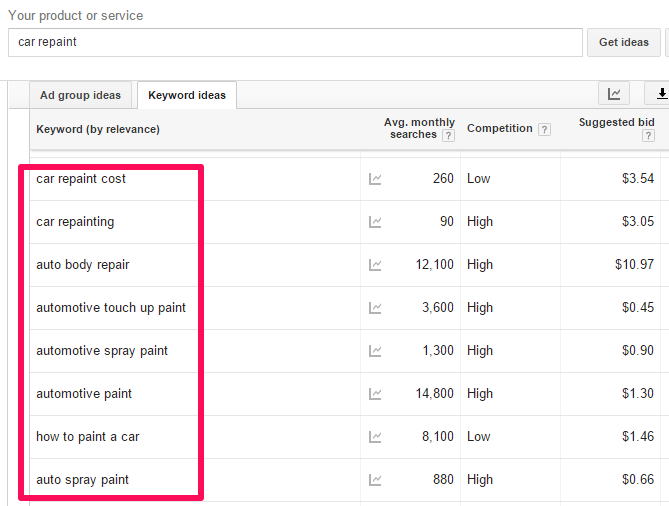
Apart from using Google Keyword Planner to research your keywords, you could also check which keywords your competitors are targeting.
It’s easy to do. First, head over to SEMrush. Type your competitor’s URL in the search box.
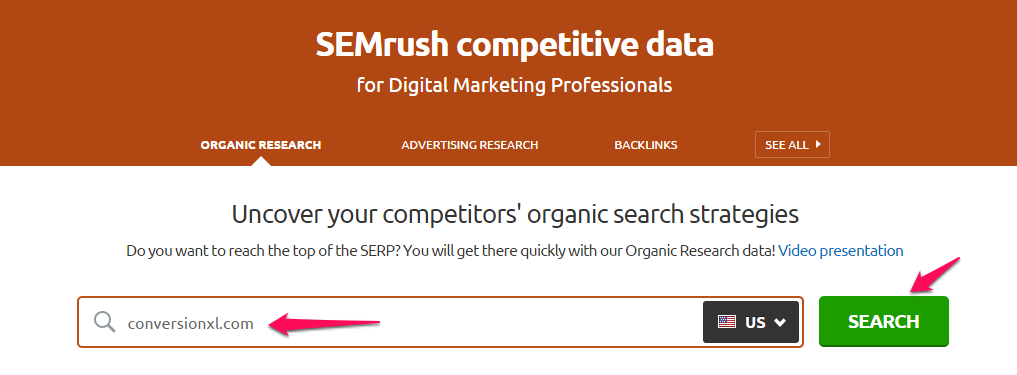
Next, click the green “search” button. Scroll down to find the primary keywords that your competitor is ranking for:
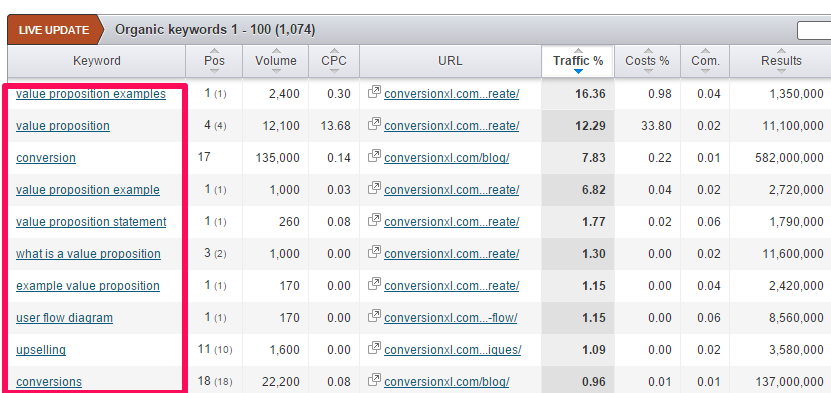
Keyword research is still pretty relevant. But, in order to stay safe, focus on the user intent behind the search, not just the keywords themselves.
11. Paid search improves organic results
Can AdWords PPC help in organic rankings?
I don’t think so. There is no apparent correlation between organic rankings and paid rankings. They function on different terrain. The organic search results come from the index database, while PPC’s sponsored links are based on your bid and total investment.
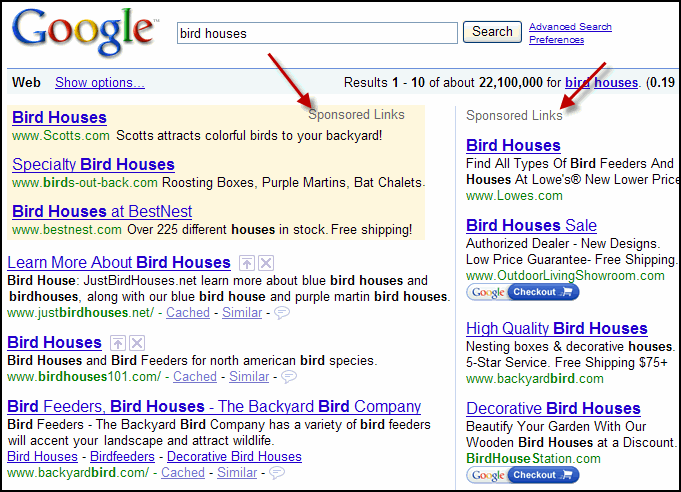
According to a report by MarketLive, the conversion rate of traffic to paid ads is actually 35% orf mediathek video herunterladen. This is way higher than organic traffic.
With paid ads, you can target more keywords and easily test different campaigns. More importantly, you can strengthen your brand identity when your paid ad appears above the search rankings.
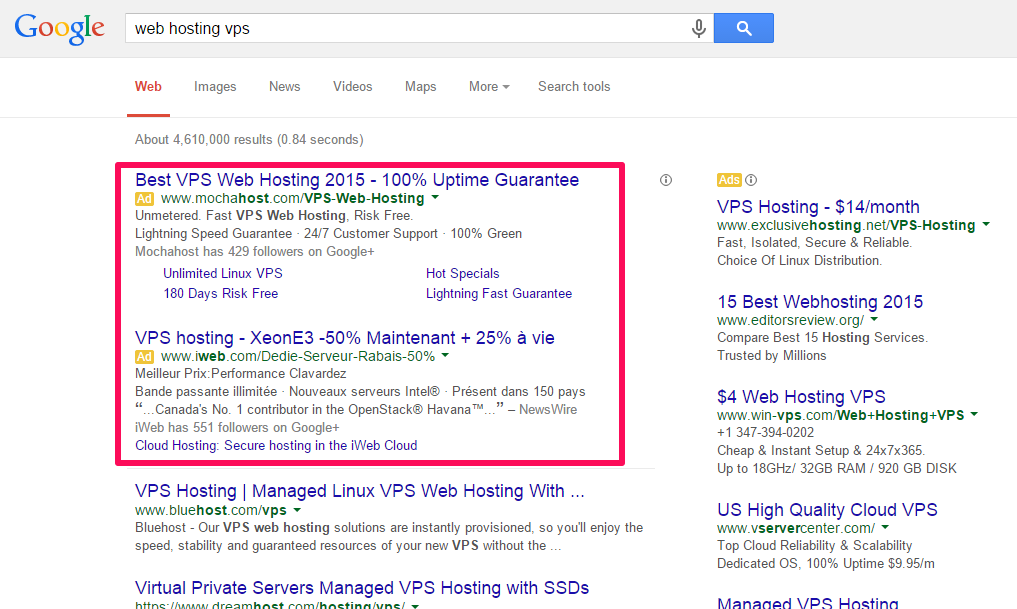
Aaron Bradley explained that paid search can help define and refine the keywords that you target organically, through accurate data. After all, it’s much easier to measure the ROI of a paid search link than that of a free organic listing.
He went on to say that the click-through rates on paid ads will give you insight into the best keywords to optimize for organic searches.
So, there is no doubt that paid search can help in improving the conversion rate of organic results, but it won’t help with rankings.
12. Claiming your Google listings will increase your search traffic
Google Places are official business listings that include your business phone number and address. Claiming your local Google Place listing is very important.
You’re basically telling Google to list your business in the area where you have the most customers or clients.
After filling out the form, you’ll be asked to go through the verification process, via an immediate phone call to verify your pin number.
But, merely listing your business in Google local will not increase your search rankings. Some of the things you’ll need to do to get the rankings that you want are:
i). Stay consistent: Copyblogger Media said that neither Google nor Bing is happy with inconsistency. In other words, you shouldn’t change your business name tomorrow, come back to Google local, get listed and, in the next few months, change to “Something Else LLC.”
In order to remain consistent, use the same details that you do in guest blogging, on your social media profiles and on all websites where you’re featured.
ii). Local outreach: Get other people to talk about your listing on the map. Ask them to link to your local listing page. You can always use Open Site Explorer to find who linked to your site and notify them about your business listing.
Punch Bug Marketing highlights 5 ways to improve your local search rankings:

13. Google hates black hat link building
What so many SEOs call “black hat” really isn’t. In fact, most of what you’re doing that seems like “white hat” is really “black” in disguise.

Who has the best definition of SEO best practices and guidelines that you should follow for your site? Google. Here’s what they said on the Google webmasters blog.

You can find Bing’s guidelines right here.
First and foremost, black hat SEO has more to do with the manner by which you build links, write content, network or connect with other people. Many people think that leaving comments on blogs is a black hat SEO technique, but that’s not true.

The question to ask is this: what is the value of my comments to the site? Am I adding value or just looking for links?
If you’re not adding value, then that’s a black hat technique.
Did you know that most people use guest blogging in the wrong way? Believe me, that’s black hat, too. Any SEO practice that isn’t centered on the user’s point of view is black hat.
White hat SEO practices may take some time to show results, but they’ll be sustainable.
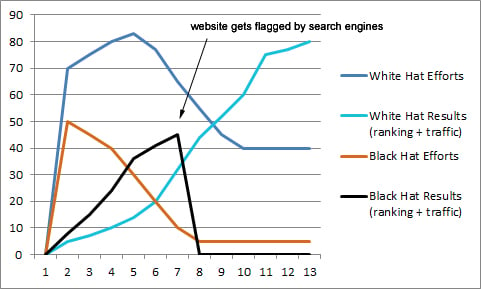
I don’t recommend link buying, because Google listed it as a black hat technique tonies lieder. But, if the link will benefit the users, should you go ahead and do it anyway?
Of course. Google’s goal is to give search users the right information, so they’ll come back tomorrow to conduct another search. That’s how Google makes its money, because eventually its ads will be clicked.
So, white hat SEO practices are those that are concerned about the user experience and Google loves them.
For example, social media marketing is white hat, but social media scheming, whereby you try to manipulate search rankings by getting as many people as possible to mention, tweet or share your link on their social profiles, is black hat.
Google doesn’t hate the platform – rather, it hates what is done on the platform. A WordPress blog is a great platform, but what happens there could be black or white hat.
14. Long form content = top rankings
Long-form content can improve rankings, but it’s not that simple. As far as SEO is concerned, there are several factors that contribute to a high-quality site.

To rank higher in Google SERPs in this Hummingbird age, focus on the user’s intent and gaining editorial links. They’re the easiest routes to follow.
The thing is that people regard in-depth content as valuable. But, in reality, most long articles aren’t so valuable for the user.
The question to ask yourself is this: “Does the content page contain substantial value, when compared to other pages in search results?”
When I analyzed some top search results, I discovered that long-form content does rank, but not in the #1 position.
In summary, long-form content can improve your rankings, but here are few tips to keep in mind:
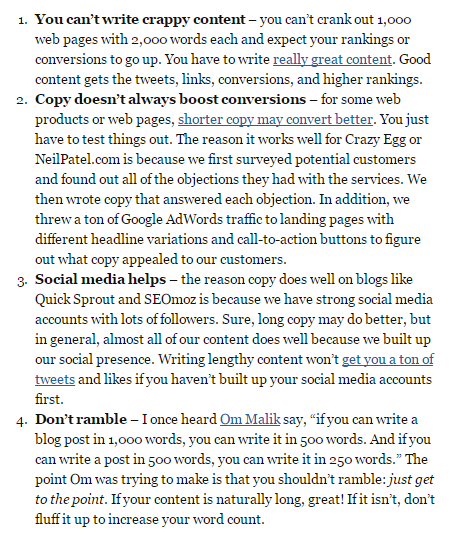
15. Linking out to authority sites sends organic visitors away
Obviously, linking out to other blogs sends your visitors away. And yet, several popular sites became successful, because they always link out to others.
For example, the blog you’re reading right now is my newest. Last month, I generated over 46,000 visitors.

I always link out to relevant and authority blogs. I don’t withhold those links, thinking that my readers will leave and never return. See how many web pages I linked to in the post excerpt below?

What I know for certain is that as long as my content is useful, practicable, in-depth and persuasive, even when readers click a link and leave, they’ll come back.
Many times, we strive to get links from authority sites, such as CNN, Mashable, Business Insider, BoingBoing and .gov and .edu sites, because we know that links from these sites will boost our search rankings. And, there are authority sites in every industry.
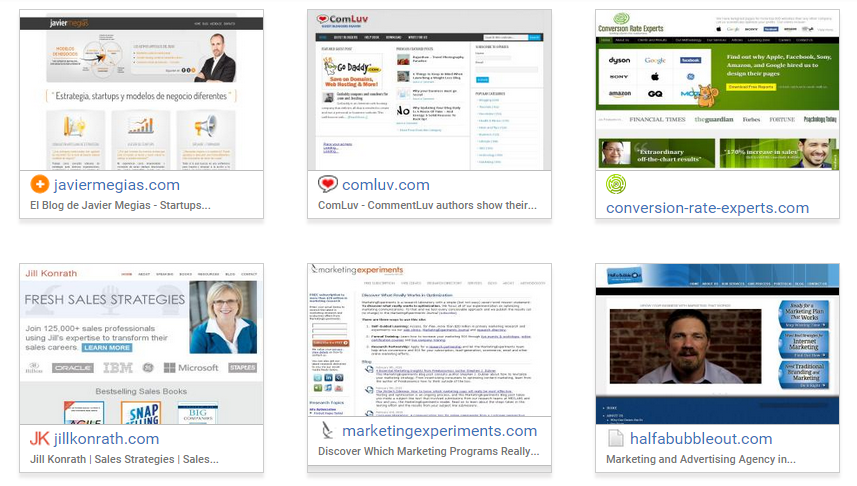
Apart from those, you can find similar authority sites to link to. Just go to similarsites.com, type in the URL for one of the authority sites (e.g., ConversionXL) and dig in.
Here are similar sites related to ConversionXL that you could link out to:
In the same way, when you link out to Google-friendly sites, especially to pages that are relevant to the content that you’re writing, Google will crawl your site and follow the links to the trusted site.
Google may not have explicitly stated that this improves your rankings, but through years of writing content and doing SEO, I’ve found it to be true.
Follow these simple tips, when linking out to authority sites, to stay safe and reap the rewards:
- Link out from a high-quality content page.
- Link out only when necessary.
- Use the brand name or URL of the authority site as your anchor text.
- Find relevant pages on authority sites and link to them serien auf handy downloaden.
- If you can, notify the site owners and bloggers when you link to them (you may get a tweet or natural link).
16. H1 tags are important elements that increase search rankings
Before Google Panda, all of the things that you did for on-page optimization carried a lot of weight in Google’s eyes. But, times are different now.
H1s are important elements, but there is no clear indication that they can boost your search rankings.
Chris Butterworth conducted an experiment to determine the effect of H1 – H6 elements on rankings. After two weeks, he discovered that the higher the number, the lower the ranking. In the words, an unstyled <p> element ranked higher than a styled <h1> element.
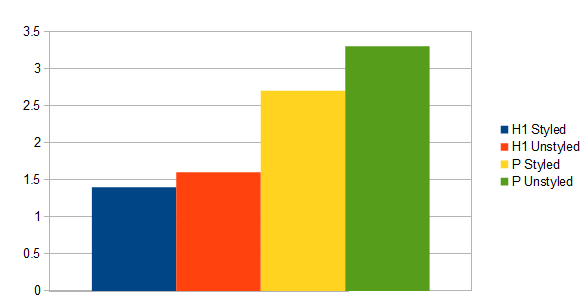
Some time ago, I watched a 5-second video, where Matt Cutts answered a very common question. The question is from Nik. Here it is:

Nik was worried that the spider might not know what’s happening on the page, because the header tags are not well-optimized.
Matt Cutts said that it doesn’t matter whether you use H1 or H2. What matters is that your page contains relevant and useful information that will address the needs of your users.
Rand Fishkin also said that heading styles no longer matter in today’s SEO, but great user experience does.
The major reason why most people obsess over <h1> styles in the internet marketing world is because they have lots of software tools for building high-converting landing pages and the majority of them can at least design a simple HTML web page.
But, in the non-internet-related industries, those guys don’t care so much about header tags, but they still give priority to content. That’s the reason why they succeed.
In all, I recommend that you use heading tags, not because you want to boost your search rankings, but because it’ll create a better experience for your users. They’ll more easily navigate your site and know the difference between the subheads and the rest of the text.
Depending on your WordPress theme or template, H1 – H3 tags will break up large chunks of text into easily digestible pieces of text.
And remember, when your readers are excited about your content and stick around, Google will reward you with better search rankings and increased traffic.
17. Social signal isn’t a ranking factor
Do links from Facebook, Twitter and other social media networks affect ranking? Are social signals a part of Google’s ranking factor? In an earlier Whiteboard Friday, Rand Fishkin answered the question.

Brian Dean did a great job at highlighting Google’s 200 ranking factors. But, is that all there is to it?
I don’t think so. Social metrics play an important role in bringing together all other ranking factors and making them work together.
The good thing about social metrics is that they can be tracked and measured with precision, unlike your personal brand.
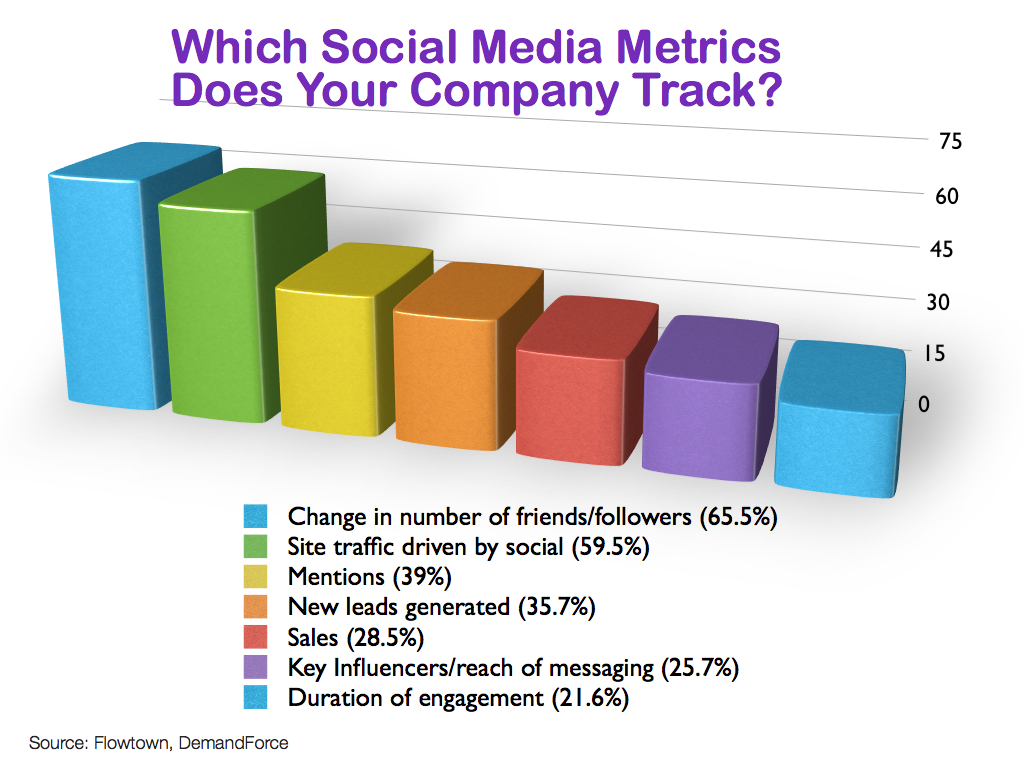
Personally, I believe there is a correlation between social and search. Both Google and Bing use data from social sites to determine how useful your site is and where to rank it.
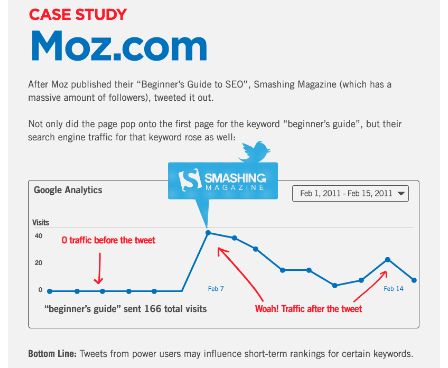
The effect of social signals on rankings may not be noticeable, because social signals don’t pass direct link juice to a particular page. Moz started ranking for “beginner’s guide to SEO,” right after Smashing Magazine tweeted that post to thousands of followers.
Although the improved rankings may not last long, when power users share your page on social platforms, you’ll experience a sizable increase in search traffic vollmachten.
Shrusti benefited immensely from social media signals as well. He went from page 400 to page 1, just by being active and creating a great experience for the target audience.

Note that it takes time to actually see improved search traffic and rankings, especially when you solely focus on social signals.
I recommend that you use SEO, blogging and social media marketing to increase your web traffic, while you build your brand along the way.
Conclusion
I’ve had my own fair share of SEO failure, but I’m always inspired to learn and upgrade my skills.
Reading other blogs and learning from knowledgeable content marketers can help you discover your own passion and embrace change. The web is a dynamic platform, after all.
But, you’ve got to do it with discretion. Most of the advice out there isn’t borne out of deep understanding about search engine optimization and how search engines work.
I’m sure that these 17 SEO myths will help you grow your site and find even better ways to cater to your target audience.
Do you know of any other SEO myths that keep site owners from increasing organic traffic and rankings?



